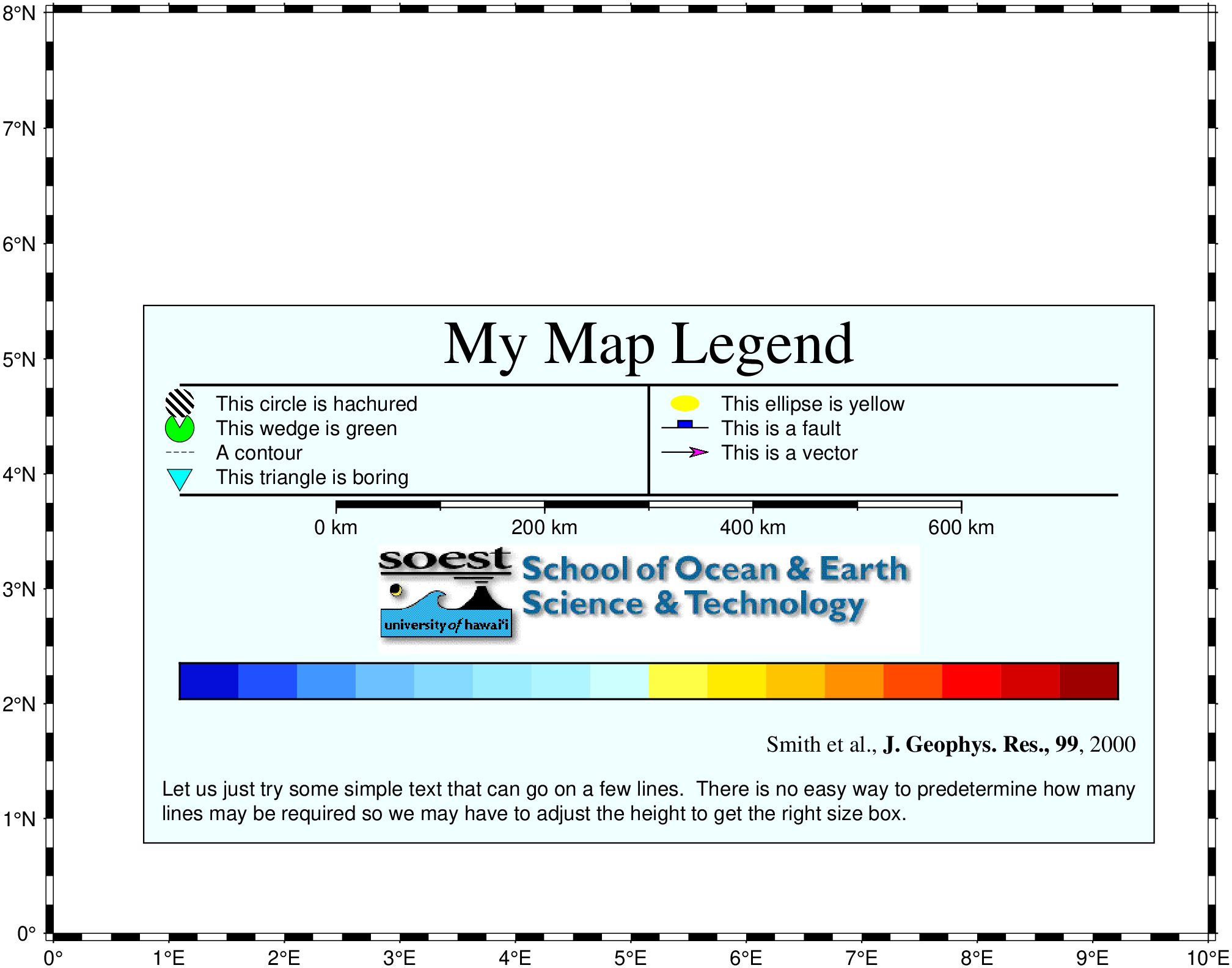
legend
legend(cmd0::String="", arg1=nothing; kwargs...)Description
Makes legends that can be overlaid on maps. It reads specific legend-related information from an input file or from a GMTdatset type. Unless otherwise noted, annotations will be made using the primary annotation font and size in effect (i.e., FONT_ANNOT_PRIMARY)
Example of a map legend, here for seismicity in the Pacific region.
Required Arguments
D or pos or position : – pos=(map=(lon,lat), inside=true, outside=true, norm=(x,y), paper=(x,y), justify=code, offset=XX)
Defines the reference point on the map for the legend using one of four coordinate systems:
Use
map=(lon,lat)for map coordinates. Requires both region and proj to be set.Use
inside=codeoroutside=codefor setting the refpoint via a 2-char justification code that refers to the (invisible) projected map bounding box. Requires both region and proj to be set.Use
norm=(x,y)for normalized bounding box coordinates (0-1). Requires both region and proj to be set.Use
paper=(x,y)for plot coordinates (append cm, inch, or point).
Use width=(width,height) to set the width (and height) of the legend box in plot coordinates (inches, cm, etc.). If height is zero or not given then we estimate height based the expected vertical extent of the items to be placed. By default, the anchor point on the legend is assumed to be the bottom left corner (:BL), but this can be changed by appending justify followed by a 2-char justification code justify (see text). Note: If inside is used then justify defaults to the same as anchor, if outside is used then justify defaults to the mirror opposite of anchor. Use spacing=val to change the line-spacing factor in units of the current font size [1.1].
Optional Arguments
B or axes or frame
Set map boundary frame and axes attributes. Default is to draw and annotate left, bottom and vertical axes and just draw left and top axes. More at frame
C or clearance : – clearance=(dx,dy)
Sets the clearance between the legend frame and the internal items [4p/4p].F or box : – box=(clearance=val, fill=color, inner=true, pen=pen, rounded=true, shaded=XX)
Without further options, draws a rectangular border around the scale usingMAP_FRAME_PEN; specify a different pen withpen=pen(see Pen attributes).fill=colorwhere color is any valid color setting (see Setting color), to fill the scale panel [no fill].clearance=valwhere val is either gap or (xgap,ygap), or (lgap,rgap,bgap,tgap) where these items are uniform, separate in x- and y-direction, or individual side spacings between scale and border.inner=trueto draw a secondary, inner border as well. We use a uniform gap between borders of 2p and theMAP_DEFAULTS_PENunless other values are specified (likeinner="gap/pen")rounded=trueto draw rounded rectangular borders instead, with a 6p corner radius. You can override this radius by using another value instead of true (default is 6p).shadded=trueorshadded=(dx,dy)orshadded=shadeto draw an offset background shaded region. Here, dx/dy indicates the shift relative to the foreground frame [4p/-4p]and shade sets the fill style to use for shading ("gray50").
J or proj or projection : – proj=<parameters>
Select map projection. More at proj
M or source
Modern mode only: Read both (1) the hidden auto-generated legend information file created by plotting-modules' legend option (warning: not this legend module) and (2) additional information from input file(s) given on the command line [hidden file only].
R or region or limits : – limits=(xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax) | limits=(BB=(xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax),) | limits=(LLUR=(xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax),units="unit") | ...more
Specify the region of interest. More at limits. For perspective view view, optionally add zmin,zmax. This option may be used to indicate the range used for the 3-D axes. You may ask for a larger w/e/s/n region to have more room between the image and the axes.
S or scale : scale=val
Scale all symbol sizes by a common scale.T or leg_file : leg_file=fname
Modern mode only: Write hidden legend specification file to fname.
U or time_stamp : – time_stamp=true | time_stamp=(just="code", pos=(dx,dy), label="label", com=true)
Draw GMT time stamp logo on plot. More at timestamp
V or verbose : – verbose=true | verbose=level
Select verbosity level. More at verbose
X or xshift or x_offset : xshift=true | xshift=x-shift | xshift=(shift=x-shift, mov="a|c|f|r")
Shift plot origin. More at xshift
Y or yshift or y_offset : yshift=true | yshift=y-shift | yshift=(shift=y-shift, mov="a|c|f|r")
Shift plot origin. More at yshift
p or view or perspective : – view=(azim, elev)
Default is viewpoint from an azimuth of 200 and elevation of 30 degrees.
Specify the viewpoint in terms of azimuth and elevation. The azimuth is the horizontal rotation about the z-axis as measured in degrees from the positive y-axis. That is, from North. This option is not yet fully expanded. Current alternatives are:view=??
A full GMT compact string with the full set of options.view=(azim,elev)
A two elements tuple with azimuth and elevationview=true
To propagate the viewpoint used in a previous module (makes sense only inbar3!)
More at perspective
q or inrows : – inrows=??
Select specific data rows to be read and/or written. More at
t or transparency or alpha: – alpha=50
Set PDF transparency level for an overlay, in (0-100] percent range. [Default is 0, i.e., opaque]. Works only for the PDF and PNG formats.
Legend Codes
Each legend item is described by a unique record. All records begin with a unique keyword name template that is common to all records of the same kind. We may have to use a template because keyword names cannot be repeated but several records of the same type can. Hence, when needing to repeat a record type we use, for example, symbol1, symbol2, etc... The order of the legend items is implied by the order of the records. Fourteen different record types are recognized, and the syntax for each of these records are presented below:
A or cmap or cpt : cmap=
cptname
Symbol or cell color fills may be given indirectly via a z-value which can be used for the color look-up via the given CPT cptname. You may switch to other cptname by repeating this command.B or colorbar : colorbar=(name=
cptname, offset=val, height=val[, extra="..."])
This record will plot a horizontal color bar, colorbar -style in the middle, starting atoffsetfrom the left edge, and of the givenheight. You may add any additional colorbar options as well as string inextra=opts. Any of the modifiers (here in hardcore GMT syntax) [+e[b|f][length]][+h][+m[a|c|l|u]][+n[txt]] may be appended ts a string o theheightargument, while other module options frame, shade, equal, monochrome, dpi, nolines zfile and view may be appended as optional arguments at the end of the record. See colorbar for details on all modifiers and options.C or textcolor : textcolor=
color
Specifies the color with which the remaining text is to be printed via z=value (requires a prior cmap code as well). When textcolor is used in a legend then your font specifications cannot also contain a color specification since we will append ,textcolor to the font. Use - to reset to default color.D or hline : hline=(pen=
pen, offset=val)
The hline record results in a horizontal line with specifiedpenacross the legend with one quarter of the line-spacing left blank above and below the line. Two gaps ofoffsetunits are left blank between the horizontal line and the left and right frame sides [0]. If no pen is given we useMAP_GRID_PEN_PRIMARY, and ifpenis set to - then no visible line is drawn (we just remember the location as a possible start/stop point for a vertical line; see vline). To not add the quarter line-spacing before the line, add -. To not add the spacing after the line, add +. For no spacing at all, add = [Default places a quarter line-spacing both before and after the line].F or fill : fill=
fill1| fill=(fill1, fill2, ...)
Specify fill (color of pattern) for cells. Alternatively, you can specify an indirect color via z=value (requires a prior cmap code). If only fill1 is given then it is used to fill the entire row, otherwise give one fill value for each active column (see ncol). If any fill is - then no fill takes place [Default].G or gap or vspace : vspace=
space
This record specifies a vertical gap of the given length. In addition to the standard units (i, c, p) you may use l for lines. A negativegapwill move the current line upwards (thus closing a gap).H or header : header=(text=
txt, [font=font])
This record plots a centered text string using the specified font parameters. Iffontis not used we default to size and fonttype ofFONT_TITLE.I or image : image=(image=
fname, width=val, justify=code)
Place an EPS or raster image in the legend justified relative to the current point. The imagewidthdetermines the size of the image on the page andcodeis 2-chars positioning code.L or label : label=(label=
text, justify=code[,font=font])
Plots a (L)eft, (C)entered, or (R)ight-justifiedtextstring within a column using the specified font parameters.codeis one of :L, :C or :R. Iffontis not used we default to size and fonttype ofFONT_TITLEM or map_scale : map_scale=([lon=
val,] lat|y=val, length=val[,region=?, proj=?, box=?])
Place a map scale in the legend. Specifylon lat, the point on the map where the scale applies (lonis only meaningful for certain oblique projections. Givelength=val, the length of the scale in km (for other units append e (meter), f (foot), M (mile), n (nautical mile), or u (survey foot)). Append +f for a fancy map scale [Default is plain]. All these cases using a unit imply thatvalmust be a string. Append +l to the length to select the default label which equals the distance unit (meter, feet, km, miles, nautical miles, survey feet) and is justified on top of the scale [t]. Change this by giving your own label (append +llabel). Change label alignment with +aalign (choose among l(eft), r(ight), t(op) , and b(ottom)). Apply +u to append the unit to all distance annotations along the scale. If you want to place a map panel behind the scale, add a suitable box panel option (seebasemapfor details on panels as well as map scale modifiers). All +modifiers must be appended tolengthto make a single string argument. If the region proj supplied to the module is different than the projection needed for the scale (or not given at all, e.g., with pos=(x=(...),), supply the two optional region and proj settings as well.N or ncols : ncols=
val
Change the number of columns in the legend [1]. This only affects the printing of symbols (symbol) and labels (label). The number of columns stay in effect until ncols is used again. To get columns of unequal width, instead provide the relative width of each column separated by whitespace in the form of a string as in relwidth1 relwidth2 … relwidthn. The sum of these widths are equated to the legend width set via position. If no argument is given the we setncolsto 1.P or paragraph : paragraph=true | paragraph=
options
Start a new text paragraph by specifying all the parameters needed (see textparagraph record description). Note that the module knows what all those values should be, so normally you can just useparagraph=true. If you need to set at least one of the parameters directly, you must specify all and set the ones you want to leave at their default value to -.S or symbol : symbol=(marker=
name, [dxleft=val,] size=val[fill=fill, pen=pen] [, dxright, label=text])
Plots the selected symbol with specified diameter, fill, and outline (see plot). The symbol is centered atdx_leftfrom the left margin of the column, with the optional explanatory label startingdx_rightfrom the margin, printed withFONT_ANNOT_PRIMARY. Ifdx_leftis not given then it is automatically computed from half the largest symbol size. Ifdx_rightis not given then it is automatically computed as 1.5 times the largest symbol size. Thefillcan be a pen of pattern or may be specified indirectly via z=value and the color is assigned via the CPT look-up (requires a prior cmap code). When plotting just a symbol, without text,dx_rightandlabelcan be omitted. Thedx_leftvalue can also be given as a justification code L, C, or R which justifies the symbol with respect to the current column. If no arguments are given to symbol then we simply skip to the next column. Three plot symbols may take special modifiers: front (f), quoted line (q) and vector (v). You can append modifiers to the symbol and affect how the fronts, quoted lines and vectors are presented (see plot man page for modifiers). The module will determine default settings for all modifiers and secondary arguments if not provided. A few other symbols (the rectangles, ellipse, wedge, mathangle) may take more than a single argument size. Note that for a line segment you should use the horizontal dash symbol (-). If just a single size if given then we will provide reasonable arguments to plot the symbol (See Defaults). Alternatively, combine the required arguments into a single, comma-separated string and use that as the symbol size (again, see plot for details on the arguments needed).T or text[xx] : text[xx]=
text
One or more of these text records with paragraph-text printed withFONT_ANNOT_PRIMARY. To specify special positioning and typesetting arrangements, or to enter a paragraph break, use the optional paragraph record. NOTE: since we cannot repeat keyword names, if we want to provide several text strings we must use different keyword names. Hence thetext[xx]that means we can repeat this option withtext1,text2, etc...V or vline : vline=(pen=
pen[, offset=val])
Draws a vertical line between columns (if more than one) using the selectedpen. Here,offsetis analogous to the offset for the hline records but in the vertical direction [0]. The first time vline is used we remember the vertical position of the last hline line, and the second time vline is set we draw from that past location to the most recent location of the hline line. Thus, hline must be used to mark the start and stop of a vertical line (so vline must follow hline). If no horizontal line is desired simply give - aspento hline.
figname or savefig or name : – figname=
name.png
Save the figure with thefigname=name.extwhereextchooses the figure image format.
The function GMT.mk_legend(kwargs...) can be used to generate the hard core GMT Legend Codes, which in turn can be written to a file and feed to this module as input. It can also be used in debug to check that the appropriate ASCII codes were generated.
Defaults
When attributes are not provided, or extended symbol information (for symbols taking more than just an overall size) are not given as comma-separated quantities, we will provide the following defaults:
Front: The size argument is length[/gap[ticklength]]. Front symbol is left-side (here, that means upper side) box, with ticklength set 30% of the given symbol length (if not specified separately), and *gap defaulting to -1 (one entered front symbol) if not specified. Modifiers to the symbol argument can be provided.
Vector: Head size is 30% of given symbol size.
Ellipse: Minor axis is 65% of major axis (the symbol size), with an azimuth of 0 degrees.
Rectangle: Height is 65% of width (the symbol size).
Rotated rectangle: Same, with a rotation of 30 degrees.
Rounded rectangle: Same as rectangle, but with corner radius of 10% of width.
Mathangle: Angles are -10 and 45 degrees, with arrow head size 30% of symbol size.
Wedge: Angles are -30 and 30 degrees.
Note On Legend Height
As position suggests, leaving the height off forces a calculation of the expected height. This is an exact calculation except in the case of legends that place paragraph text. Here we simply do a first-order estimate of how many typeset lines might appear. Without access to font metrics this estimate will occasionally be off by 1 line. If so, note the reported height (with verbose) and specify a slightly larger or smaller height in position.
Examples
To add an example of a legend to a Mercator plot with the given specifications:
using GMT
makecpt("-Cpanoply -T-8/8 > tt.cpt")
legend((
vspace=-0.25,
header=(text="My Map Legend", font=(24,"Times-Roman")),
hline=(pen=1, offset=0.5),
ncolumns=2,
vline=(pen=1, offset=0),
symbol1=(marker=:circ, size=0.4, dx_left=0.25, fill="p300/12", dx_right=0.75, text="This circle is hachured"),
symbol2=(marker=:ellipse, size=0.4, dx_left=0.25, fill=:yellow, dx_right=0.75, text="This ellipse is yellow"),
symbol3=(marker=:wedge, size=0.4, dx_left=0.25, fill=:green, pen=0.25, dx_right=0.75, text="This wedge is green"),
symbol4=(marker=:fault, size=0.65, dx_left=0.25, fill=:blue, dx_right=0.75, text="This is a fault"),
symbol5=(marker="-", size=0.4, dx_left=0.25, pen=(0.25,:dash), dx_right=0.75, text="A contour"),
symbol6=(marker=:vector, size=0.65, dx_left=0.25, fill=:magenta, pen=0.5, dx_right=0.75, text="This is a vector"),
symbol7=(marker="i", size=0.4, dx_left=0.25, fill=:cyan, pen=0.25, dx_right=0.75, text="This triangle is boring"),
hline2=(pen=1, offset=0.5),
vline2=(pen=1, offset=0),
ncolumns2=1,
map_scale=(lon=5, lat=5, length="600+u+f"),
vspace2=0.13,
image=(width=7.5, fname="@SOEST_block4.png", justify=:CT),
vspacep3=0.13,
colorbar=(name="tt.cpt", offset=0.5, height=0.5, extra="-B0"),
label=(txt="Smith et al., @%5%J. Geophys. Res., 99@%%, 2000", justify=:R, font=(9, "Times-Roman")),
vspace4=0.25,
text1="Let us just try some simple text that can go on a few lines. There is no easy way to predetermine",
text2="how many lines may be required so we may have to adjust the height to get the right size box."
),
region=(0,10,0,8), pos=(paper=(1.25,1.25), width=14, justify=:BL, spacing=1.2),
clearance=(0.25,0.25), box=(pen=0.5, fill=:azure1),
figsize=16, proj=:Mercator, show=true
)These docs were autogenerated using GMT: v1.33.0