gridit
G = gridit(fname="", indata=nothing; method="surface", gdopts="", proj="", epsg=0, kw...)
Wrapper function to interpolate scattered data into a grid. Interpolation methods may be those of GMT and GDAL (gdal_grid).
Parameters
fname: A file name containing the source dataset to be interpolated. It must contain at least 3 columns (x y z).indata: Alternative source dataset in the form of a GMTdataset, a Mx3 matrix or a GDAL dataset.method: The interpolation method name. One of (GMT): "surface" or "minimum curvature", "triangulate", "nearneighbor", "sphtriangulate", "greenspline". The arguments: "mean", "median", "mode", "std", "highest", "lowest" will compute those amounts inside each rectangular cell.Or (GDAL): "invdist", "invdistnn", "average", "nearest", "linear", "minimum", "maximum", "range", "count", "average_distance", "average_distancepts". See [gdalgrid](https://gdal.org/programs/gdal_grid.html#gdal-grid)
Note that there is some overlap between the diverse methods. For example, the GMT's \myreflink{nearneighbor} and GDAL's
invdistapply the same algorithm (the Inverse Distance Weight) but they difer on how to select the points to do the weighted average.
gdopts: List of options, in the form of a single string, accepted by the gdal_grid utility. This option only applies to the GDAL methods.proj: An optional proj4 string describing the data's coordinate system. Note that this not imply any data projection. The input data may itself already carry this information, case in which this option is not necessary.wkt: An optional wkt string describing the data's coordinate system. Same comments asprojepsg: An optional epsg code describing the data's coordinate system. Same comments asprojkw...keyword=value arguments. These are used to pass options that are specific to a particular GMT interpolation methods. The user must consult individual manual pages to learn about the available possibilities. Two very important (actually, mandatory) options are theregion=...and theinc=...that select the grid limits and the grid resolution. However, if they are not provided (or only one of them is) we make a very crude estimate based on data limits and point density. But this should only be used for a very exploratory calculation.preproc: This option only applies to themethod=:surfaceand means that the data is previously passed through one ofblock*modules to decimate the data in each cell as strongly advised by the surface program.preproc=truewill use blockmean. To use any of the other two, pass its name as value. e.g.preproc="blockmedian".
Returns
A GMTgrid or nothing if file was writen on disk.
Examples
using GMT
# Interpolate cashed data ship_15.txt
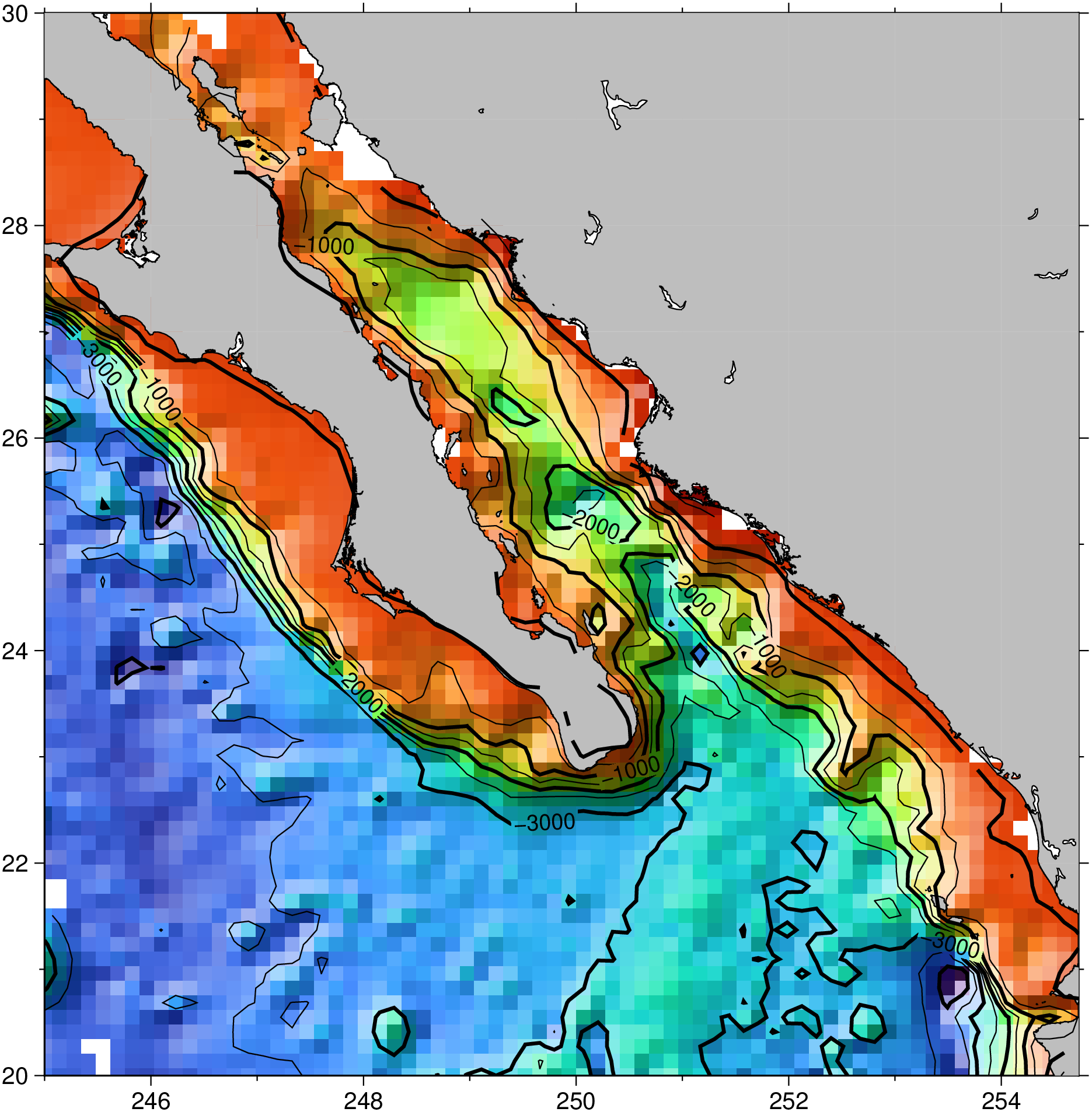
G = gridit("@ship_15.txt", method=:surface, mask=0.3, preproc=true, V=:q);
# Make a base image from gridded data
grdimage(G, shade=true, coast=(land=:gray, shore=0.5))
# Add automatic contours
grdcontour!(G, show=true)See Also
blockmean, blockmedian, surface, triangulate, nearneighbor
These docs were autogenerated using GMT: v1.29.0