grid2tri
D = grid2tri(G, G2=nothing; bottom=false, downsample=0, isbase=false, ratio=0.01,
thickness=0.0, wall_only=false, top_only=false, geog=false)::GMTfvTriangulate the surface defined by the grid G, and optionally the bottom surface G2.
Other than the triangulation, this function computes also a vertical wall between G and G2, or between G and constant level or a constant thickness. Optionally, computes only the vertical wall or the full closed bodie (that is, including the bottom surface).
The output of this function can be used in plot3d to create 3D views of volume layer.
NOTE: The G grid should have a out-skirt of NaNs, otherwise just use grdview with the N option.
Args
G: A GMTgrid object or a grid file name representing the surface to be triangulated.G2: An optional second grid (or file name) representing the bottom surface of the layer. Using this option makes thethicknessoption be ignored.
Kwargs
bottom: If true, fully close the body with the bottom surface. By default we don't do this because that surface is often not visible whem elevation view angle is positive. But we may want this if later we want to save this mesh in STL for importing in a 3D viewer software.downsample: If the grid is of too high resolution, files here get big and operations slow down with this and later figures may not benefit much. In those cases it is a good idea to downsample the grid. Thedownsampleoption accepts an integer reduction factor.downsample=2will shrink the grid by a factor two in each dimention,downsample=3will shrink it by a factor three etc.isbase: If true, we interpretthicknessoption as meaning a contant level value. That is, the vertical wall is computed from the sides ofGand a constant level provided via thethicknessoption.ratio: A slightly tricky parameter that determines how close the computed concave hull is to the true concave hull. A value smaller to 0.005 seems to do it but we normally don't want that close because the vertical wall obtained from this will be too jagged. The default value of 0.01 seems to work well to get a smoother concave hull but one that still fits the objective of getting a nice vertical wall. May need tweaking for specific cases.thickness: A scalar representing the layer thickness in the same units as those of the input grid. NOTE: this option is ignored when two grids are passed in input.wall_only: If true, only the vertical wall betweenGandG2, orG+thicknessis computed and returned.top_only: If true, only the triangulation ofGis returned.geog: If theGgrid has no referencing information but you know that it is in geographical coordinates setgeog=true. This information will be added to the triangulation output and is usefull for plotting purposes.
Returns
A vector of GMTdataset with the triangulated surface and vertical wall, or just the wall or the full closed body.
Example
A 3D view of the subduction in Central America.
using GMT
# Get the depth of these three cities
Gm, Gt, SJ = grdtrack("cam_slab2_dep_02.24.18.grd", [260.862 19.4326; 269.492 14.64; 275.925 9.908], f=:g).data[:,3]
# Create cylinder markers
FV_Mx = cylinder(0.2, 140, np=18, center=(260.862, 19.4326, Gm));
FV_Gt = cylinder(0.2, -Gt, np=18, center=(269.492, 14.64, Gt));
FV_SJ = cylinder(0.2, -SJ, np=18, center=(275.925, 9.908, SJ));
# Convert the subduction slab grids into a triangular mesh
D = grid2tri("cam_slab2_dep_02.24.18.grd", "cam_slab2_thk_02.24.18.grd", geog=true);
plot3(D, p=(70,30), zlabel="Depth (km)", title="Subduction in Central America", frame=:autoXYZg)
colorbar!(pos=(justify=:TR, horizontal=true, offset=(1,-2)),)
# Plot the coastlines drapped on the subducting slab
plot3!(coast(region=D, dump=true, Z="cam_slab2_dep_02.24.18.grd"), f=:g)
plot3!(FV_Mx); plot3!(FV_SJ); plot3!(FV_Gt)
text!(mat2ds([260.862 19.4326 10; 275.925 9.908 10; 269.492 14.64 10],
["Mexico City", "San José", "Guatemala"]),
f=:g, font=14, angle=110, noclip=true, outline=true, show=true)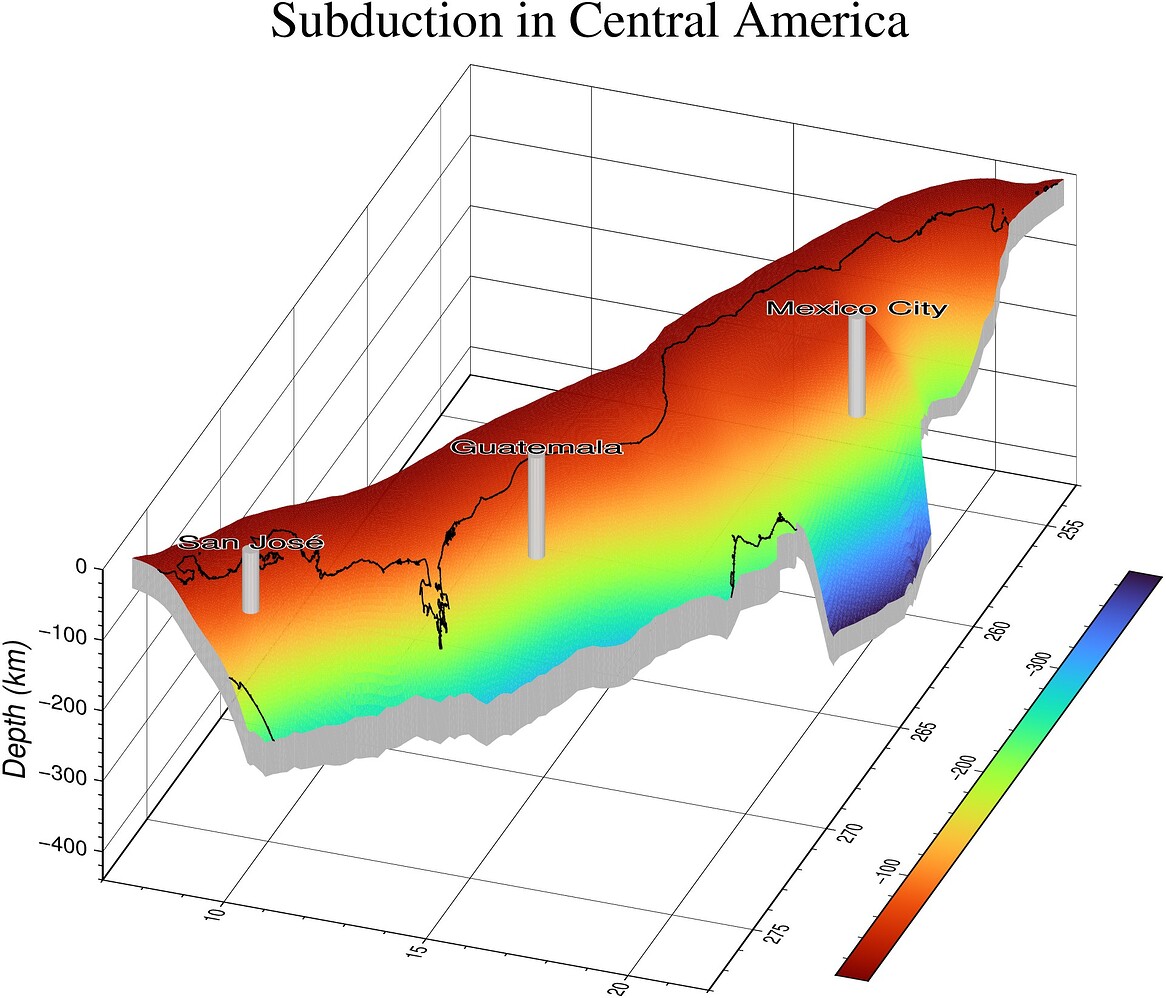
See Also
extrude, flatfv, fv2fv, loft, revolve, surf2fv
These docs were autogenerated using GMT: v1.29.0